| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
- 프로그래머스
- 백준
- 피로그래밍
- Java
- 사물인식
- yolov5
- S3
- 파이썬
- 카카오
- 페이지네이션
- AWS
- 파이썬 #백준 #BFS
- spring-boot
- jwt
- 인공지능
- CRUD
- jQuery
- 멋쟁이사자처럼
- 절차지향
- Python
- 솝트 후기
- 멋사
- 서류전형
- objectdetection
- 솝트
- EC2
- 합격후기
- MongoDB
- 면접전형
- nodejs
- Today
- Total
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
- 프로그래머스
- 백준
- 피로그래밍
- Java
- 사물인식
- yolov5
- S3
- 파이썬
- 카카오
- 페이지네이션
- AWS
- 파이썬 #백준 #BFS
- spring-boot
- jwt
- 인공지능
- CRUD
- jQuery
- 멋쟁이사자처럼
- 절차지향
- Python
- 솝트 후기
- 멋사
- 서류전형
- objectdetection
- 솝트
- EC2
- 합격후기
- MongoDB
- 면접전형
- nodejs
- Today
- Total
찔끔찔끔씩😎
[웹개발의 봄, Spring] 2주차 (2) - JPA, Repository 본문
[웹개발의 봄, Spring] 2주차 (1) - RDBMS, H2, SQL
JPA 시작하기
🔎 JPA
JPA(Java Persistence API) 는 SQL을 쓰지 않고 데이터를 생성, 조회, 수정, 삭제할 수 있도록 해주는 번역기이다.
갑자기 자바 짜다가 갑자기 SQL짜고 왔다 갔다 안해도 되게 해준다!

테이블은 Domain, SQL은 Repository
일대일 대응으로 생각하면 된다.
Repository 가 SQL 쿼리를 날려준다.
🔎 JPA 시작하기
앞서, courses라는 테이블에 title, tutor라는 컬럼을 만들었던 것을 자바로 표현하면 다음과 같다.
1. src > main > java > com.sparta.week02에 domain 이라는 패키지를 만든다.
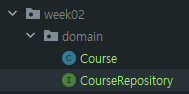
2. Course.java 클래스
@NoArgsConstructor // 기본생성자를 대신 생성해줍니다.
@Entity // 테이블임을 나타냅니다.
public class Course {
@Id // ID 값, Primary Key로 사용하겠다는 뜻입니다.
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) // 자동 증가 명령입니다.
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false) // 컬럼 값이고 반드시 값이 존재해야 함을 나타냅니다.
private String title;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String tutor;
public String getTitle() {
return this.title;
}
public String getTutor() {
return this.tutor;
}
public Course(String title, String tutor) {
this.title = title;
this.tutor = tutor;
}
}
getter만 필요하다. setter은 Repository에서 다 해주기 때문이다.
3. CourseRepository.java 인터페이스
public interface CourseRepository extends JpaRepository<Course, Long> {
}JpaRepository<Course,Long>: Course라는 녀석의 Id는 Long타입이다.
Interface란?
- JPA는 Repository를 통해서만 사용할 수 있다.
- 인터페이스는 클래스에서 멤버 변수가 빠진, 메소드 모음집!
🔎 JPA 사용해보기
1. SQL이 보이도록 application.properties를 설정한다.
: JPA가 자바를 SQL로 어떻게 바꾸는지 확인해볼라고~
spring.jpa.show-sql=true2. Week02Application.java의 main 함수 아래에 JPA 실행 코드를 작성한다.
// 테이블 생성
Course course1 = new Course("웹개발의 봄","남병관");
// 테이블에 저장
repository.save(course1);
// 테이블 조회
List<Course> courseList = repository.findAll();
for(int i =0;i<courseList.size();i++){
Course c = courseList.get(i);
System.out.println(c.getTitle());
System.out.println(c.getTutor());
}
// id 로 찾고 싶을 때: repository.findById();3. H2 웹콘솔에 접속해서 course 테이블을 확인한다.
상속
🔎 상속이란?
"extends"는 "클래스의 상속" 이라는 개념인데요. "이미 만들어둔거 가져다 쓰자!" 라고 선언하는 것입니다.
생성일자, 수정일자 (Timestamped) 로 상속 연습해보자.
1. Timestamped.java
@MappedSuperclass // 상속했을 때, 컬럼으로 인식하게 합니다.
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class) // 생성/수정 시간을 자동으로 반영하도록 설정
public abstract class Timestamped {
@CreatedDate // 생성일자임을 나타냅니다.
private LocalDateTime createdAt;
@LastModifiedDate // 마지막 수정일자임을 나타냅니다.
private LocalDateTime modifiedAt;
}abstract: 상속으로만 사용할 수 있는 클래스라는 뜻
2. Course.java
- 1의 클래스를 이제 Course에서 사용하기 위해 상속하도록 한다.
public class Course extends Timestamped{
3. Week02Application.java
- 생성일자, 수정일자를 자동으로 업데이트 해주기 위해 추가적으로 필요한 @EnableJpaAuditing
@EnableJpaAuditing //생성일자, 수정일자가 자동으로 업데이트 되기 위해 필요함.
@SpringBootApplication
public class Week02Application {
4. H2 웹 콘솔에서 확인해본다.
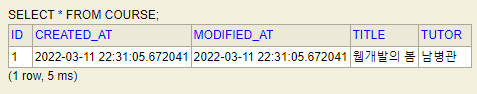
JPA 심화
🔎 JPA CRUD
CRUD란 정보관리의 기본 기능으로, 생성(Create), 조회(Read), 변경(Update), 삭제(Delete)를 말한다.
🔎 Create, Read
// 데이터 저장하기
repository.save(new Course("프론트엔드의 꽃, 리액트", "임민영"));
// 데이터 전부 조회하기
List<Course> courseList = repository.findAll();
for (int i = 0; i < courseList.size(); i++) {
Course course = courseList.get(i);
System.out.println(course.getId());
System.out.println(course.getTitle());
System.out.println(course.getTutor());
}
// 데이터 하나 조회하기
Course course = repository.findById(1L).orElseThrow(
() -> new IllegalArgumentException("해당 아이디가 존재하지 않습니다.")
);Update, Delete 전에 Service의 개념을 다루고 넘어가야 한다.
🔎 Service
스프링의 구조는 3가지 영역으로 나눌 수 있다.
- Controller : 가장 바깥 부분, 요청/응답을 처리함
- Service : 중간 부분, 실제 중요한 작동이 많이 일어나는 부분
- Repository : 가장 안쪽 부분, DB와 맞닿아 있음
🔎 Update
Update는 Service에 작성한다.
1. Course 클래스에 update 메소드를 추가한다.
public void update(Course course) {
this.title = course.title;
this.tutor = course.tutor;
}2. src > main > java > com.sparta.week02 > service 패키지 생성한다.
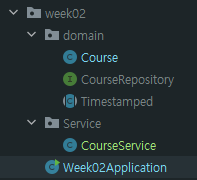
3. CourseService.java
@Service // 스프링에게 이 클래스는 서비스임을 명시
public class CourseService {
// final: 서비스에게 꼭 필요한 녀석임을 명시
private final CourseRepository courseRepository;
// 생성자를 통해, Service 클래스 생성 시 Repository를 넣어주도록
// 스프링에게 알려줌
public CourseService(CourseRepository courseRepository) {
this.courseRepository = courseRepository;
}
//------Repository를 쓸 수 있게 스프링이 넘겨줍니다. ------
@Transactional // SQL 쿼리가 일어나야 함을 스프링에게 알려줌
public Long update(Long id, Course course) { // 어떤 id를 업데이트?
Course course1 = courseRepository.findById(id).orElseThrow(
() -> new IllegalArgumentException("해당 아이디가 존재하지 않습니다.")
);
course1.update(course);
return course1.getId();
}
}4. main에서 잘 작동하는지 확인해봅시다~
@Bean
public CommandLineRunner demo(CourseRepository courseRepository, CourseService courseService) {
return (args) -> {
courseRepository.save(new Course("프론트엔드의 꽃, 리액트", "임민영"));
System.out.println("데이터 인쇄");
List<Course> courseList = courseRepository.findAll();
for (int i=0; i<courseList.size(); i++) {
Course course = courseList.get(i);
System.out.println(course.getId());
System.out.println(course.getTitle());
System.out.println(course.getTutor());
}
Course new_course = new Course("웹개발의 봄, Spring", "임민영");
courseService.update(1L, new_course);
courseList = courseRepository.findAll();
for (int i=0; i<courseList.size(); i++) {
Course course = courseList.get(i);
System.out.println(course.getId());
System.out.println(course.getTitle());
System.out.println(course.getTutor());
}
};
}🔎 Delete
바로 Repository를 통해서 해주면 된다.
courseRepository.deleteAll();'Server > Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [웹개발의 봄, Spring] 3주차 (1) - 타임라인 서비스 서버 완성하기 (0) | 2022.03.16 |
|---|---|
| [웹개발의 봄, Spring] 2주차 (3) - API, Lombok, DTO (0) | 2022.03.13 |
| [웹개발의 봄, Spring] 2주차 (1) - RDBMS, H2, SQL (0) | 2022.03.11 |
| [웹개발의 봄, Spring] 1주차 (2) - 자바 기초 문법, 브라우저, Gradle (0) | 2022.03.09 |
| [웹개발의 봄, Spring] 1주차 (1) - 웹과 스프링 기본 개념 (0) | 2022.03.08 |



